Difference between revisions of "Master Level Theses"
(→BioSignal Analysis) |
(→Sleep Staging) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
{{Project template | {{Project template | ||
|title=Development of a computer-assisted CAP (Sleep cyclic alternating pattern) scoring method | |title=Development of a computer-assisted CAP (Sleep cyclic alternating pattern) scoring method | ||
| − | |tutor=[[User:MatteoMatteucci|Matteo Matteucci]] ([mailto:matteucc%40%65%6c%65%74%2e%70%6f%6c%69%6d%69%2e%69%74 email]), | + | |tutor=[[User:MatteoMatteucci|Matteo Matteucci]] ([mailto:matteucc%40%65%6c%65%74%2e%70%6f%6c%69%6d%69%2e%69%74 email]), Martin Mendez ([mailto:martin.mendez@polimi.it email]), Anna Maria Bianchi ([mailto:annamaria.bianchi@polimi.it email]), Mario Terzano (Ospedale di Parma) |
|description=In 1985, Terzano describes for the first time the Cyclic Alternating Pattern [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cyclical_alternating_pattern] during sleep and, nowadays, CAP is widely accepted by the medical community as basic analysis of sleep. The CAP evaluation is of fundamental importance since it represents the mechanism developed by the brain evolution to monitor the inner and outer world and to assure the survival during sleep. However, visual detection of CAP in polisomnography (i.e., the standard procedure) is a slow and time-consuming process. This limiting factor generates the necessity of new computer-assisted scoring methods for fast CAP evaluation. This thesis deals with the development of a Decision Support System for CAP scoring based on features extraction at multi-system level (by statistical and signal analysis) and Pattern Recognition or Machine Learning approaches. This may allow the automatic detection of CAP sleep and could be integrated, through reinforcement learning techniques, with the corrections given by physicians. | |description=In 1985, Terzano describes for the first time the Cyclic Alternating Pattern [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cyclical_alternating_pattern] during sleep and, nowadays, CAP is widely accepted by the medical community as basic analysis of sleep. The CAP evaluation is of fundamental importance since it represents the mechanism developed by the brain evolution to monitor the inner and outer world and to assure the survival during sleep. However, visual detection of CAP in polisomnography (i.e., the standard procedure) is a slow and time-consuming process. This limiting factor generates the necessity of new computer-assisted scoring methods for fast CAP evaluation. This thesis deals with the development of a Decision Support System for CAP scoring based on features extraction at multi-system level (by statistical and signal analysis) and Pattern Recognition or Machine Learning approaches. This may allow the automatic detection of CAP sleep and could be integrated, through reinforcement learning techniques, with the corrections given by physicians. | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
|number=1-2 | |number=1-2 | ||
|cfu=20 | |cfu=20 | ||
| − | |image= | + | |image=CAP_Sleep_Staging.jpg}} |
===== Brain-Computer Interface ===== | ===== Brain-Computer Interface ===== | ||
Revision as of 17:00, 8 January 2009
Here you can find proposals for master thesis (20 CFU for each student)
Contents
BioSignal Analysis
Sleep Staging
| Title: | Development of a computer-assisted CAP (Sleep cyclic alternating pattern) scoring method | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | In 1985, Terzano describes for the first time the Cyclic Alternating Pattern [1] during sleep and, nowadays, CAP is widely accepted by the medical community as basic analysis of sleep. The CAP evaluation is of fundamental importance since it represents the mechanism developed by the brain evolution to monitor the inner and outer world and to assure the survival during sleep. However, visual detection of CAP in polisomnography (i.e., the standard procedure) is a slow and time-consuming process. This limiting factor generates the necessity of new computer-assisted scoring methods for fast CAP evaluation. This thesis deals with the development of a Decision Support System for CAP scoring based on features extraction at multi-system level (by statistical and signal analysis) and Pattern Recognition or Machine Learning approaches. This may allow the automatic detection of CAP sleep and could be integrated, through reinforcement learning techniques, with the corrections given by physicians.
| |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Martin Mendez (email), Anna Maria Bianchi (email), Mario Terzano (Ospedale di Parma) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1-2 | |
| CFU: | 20 |
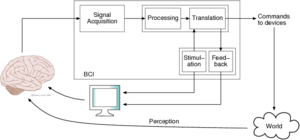
Brain-Computer Interface
| Title: | Recognition of the user's focusing on the stimulation matrix | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | A P300-based BCI stimulates the user continuously, and the detection of a P300 designates the choice of the user. When the user is not paying attention to the interface, false positives are likely. The objective of this work is to avoid this problem; the analysis of the electroencephalogram (EEG) over the visual cortex (and possibly an analysis of P300s or of other biosignals) should tell when the user is looking at the interface.
| |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Bernardo Dal Seno (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1-2 | |
| CFU: | 20 |
| Title: | Creation of new EEG training by introduction of noise | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | A BCI must be trained on the individual user in order to be effective. This training phase require recording data in long sessions, which is time consuming and boring for the user. The aim of this project is to develop algorithm to create new training EEG (electroencephalography) data from existing ones, so as to speed up the training phase.
| |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Bernardo Dal Seno (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1 | |
| CFU: | 20 |
| Title: | Real-time removal of ocular artifact from EEG | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | In a BCI based on electroencephalogram (EEG), one of the most important sources of noise is related to ocular movements. Algorithms have been devised to cancel the effect of such artifacts. The project consists in the in the implementation in real time of an existing algorithm (or one newly developed) in order to improve the performance of a BCI.
| |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Bernardo Dal Seno (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1 | |
| CFU: | 10-20 |
| Title: | Aperiodic visual stimulation in a VEP-based BCI | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | Visual-evoked potentials (VEPs) are a possible way to drive the a BCI. This projects aims at maximizing the discrimination between different stimuli.
| |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Bernardo Dal Seno (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1 | |
| CFU: | 20 |
| Title: | Driving an autonomous wheelchair with a P300-based BCI | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | This project pulls together different Airlab projects with the aim to drive an autonomous wheelchair (LURCH) with a BCI, through the development of key software modules. The work will be validated with live experiments.
| |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Bernardo Dal Seno (email) | |
| Start: | November 2008 | |
| Number of students: | 1 | |
| CFU: | 5-20 |
| Title: | Online automatic tuning of the number of repetitions in a P300-based BCI | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | In a P300-based BCI, (visual) stimuli are presented to the user, and the intention of the user is recognized when a P300 potential is recognized in response of the desired stimulus. In order to improve accuracy, many stimulation rounds are usually performed before making a decision. The exact number of repetitions depends on the user and the goodness of the classifier, but it is usually fixed a-priori. The aim of this project is to adapt the number of repetitions to changing conditions, so as to achieve the maximum accuracy with the minimum time.
The work will be validated with live experiments.
| |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Bernardo Dal Seno (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1 | |
| CFU: | 5-20 |
Machine Learning
| Title: | Reinforcement Learning in Poker | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | In this years, Artificial Intelligence research has shifted its attention from fully observable environments such as Chess to more challenging partially observable ones such as Poker.
Up to this moment research in this kind of environments, which can be formalized as Partially Observable Stochastic Games, has been more from a game theoretic point of view, thus focusing on the pursue of optimality and equilibrium, with no attention to payoff maximization, which may be more interesting in many real-world contexts. On the other hand Reinforcement Learning techniques demonstrated to be successful in solving both fully observable problems, single and multi-agent, and single-agent partially observable ones, while lacking application to the partially observable multi-agent framework. This research aims at studying the solution of Partially Observable Stochastic Games, analyzing the possibility to combine the Opponent Modeling concept with the well proven Reinforcement Learning solution techniques to solve problems in this framework, adopting Poker as testbed. | |
| Tutor: | Marcello Restelli (restelli-AT-elet-DOT-polimi-DOT-it) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1-2 | |
| CFU: | 20-40 |
| Title: | EyeBot | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | TORCS is a state-of-the-art open source racing simulator that represents an ideal bechmark for machine learning techniques. We already organized two successfull competitions based on TORCS where competitors have been asked to develop a controller using their preferred machine learning techniques. So far, the controller developed for TORCS used as input only information extracted directly from the state of the game. The goal of this project is to extend the existing controller API (see here) to use the visual information (e.g. the screenshots of the game) as input to the controllers. A successfull project will include both the development of the API and some basic imaga preprocessing to extract information from the images. | |
| Tutor: | Daniele Loiacono (loiacono-AT-elet-DOT-polimi-DOT-it), Alessandro Giusti (giusti-AT-elet-DOT-polimi-DOT-it), and Pierluigi Taddei (taddei-AT-elet-DOT-polimi-DOT-it) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1 to 2 | |
| CFU: | 20 |
| Title: | SmarTrack | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | The generation of customized game content for each player is an attractive direction to improve the game experience in the next-generation computer games. In this scenario, Machine Learning could play an important role to provide automatically such customized game content.
The goal of this project is to apply machine learning techniques for the generation of customized tracks in TORCS, a state-of-the-art open source racing simulator. The project include different activities: the automatic generation of tracks, the section of relevant features to characterize a track and the analysis of an interest measure. | |
| Tutor: | Daniele Loiacono (loiacono-AT-elet-DOT-polimi-DOT-it) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1 to 2 | |
| CFU: | 20 |
| Title: | Automatic generation of domain ontologies | [[Image:|center|300px]] |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | This thesis to be developed together with Noustat S.r.l., who are developing research activities directed toward the optimization of knowledge management services, in collaboration with another company operating in this field. This project is aimed at removing the ontology building bottleneck, long and expensive activity that usually requires the direct collaboration of a domain expert. The possibility of automatic building the ontology, starting from a set of textual documents related to a specific domain, is expected to improve the ability to provide the knowledge management service, both by reducing the time-to-application, and by increasing the number of domains that can be covered. For this project, unsupervised learning methods will be applied in sequence, exploiting the topological properties of the ultra-metric spaces that emerge from the taxonomic structure of the concepts present in the texts, and associative methods will extend the concept network to lateral, non-hierarchical relationships. | |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Andrea Bonarini (email) | |
| Start: | before November 30th | |
| Number of students: | 1-2 | |
| CFU: | 20 |
Affective Computing
| Title: | Affective VideoGames | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | The goal of this activity is to develop an interactive video game (Car game, Shoot them up, Strategic game ..) able to adapt its behaviour in order to maximize your enjoyment. The game will measure your excitement by analizing your biological signals, which mirror your emotional state. The system will be able to adjust some parameters (i.e difficulty of car game circuits, opponets strength ...) in order to keep you egnagemet constant: "In your flow zone!".
Project phases:
These projects allow to experiment with biological-data acquisition tools and videogames design. The project consists on the realization of one or more phases depending on the difficulty/cfu to be achieved and to the competences of the candidate(s) | |
| Tutor: | Cristiano Alessandro (alessandro-AT-elet-DOT-polimi-DOT-it), Simone Tognetti (togetti-AT-elet-DOT-polimi-DOT-it) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1 to 3 | |
| CFU: | 2.5 to 20 |
| Title: | Affective recognition in multimedia contexts | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | The goal of this activity is to develop an interactive multimedia application (advertisement, e-learning, reccomenadation system) able to capture your emotional state (interests, excitement, anger, joy) while whatching to images, sounds etc. The application will measure your excitement by analizing your biological signals, which mirror your emotional state. The system could be used to give feedback on the quality of multimedia content (i.e goodness of the advertisement, enjoyment of the movie ...)
Project phases:
These projects allow to experiment with biological-data acquisition tools and multimedia application design. The project consists on the realization of one or more phases depending on the difficulty/cfu to be achieved and to the competences of the candidate(s) | |
| Tutor: | Cristiano Alessandro (alessandro-AT-elet-DOT-polimi-DOT-it), Simone Tognetti (togetti-AT-elet-DOT-polimi-DOT-it) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1 to 3 | |
| CFU: | 2.5 to 20 |
| Title: | Affective robotics | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | The goal of this activity is to develop an rehabilitation robotic game able to capture your emotional state (interests, excitement, anger, joy, stress) while intereacting with the robot. The application will measure your excitement by analizing your biological signals, which mirror your emotional state. The system could be used to adapt the therapy (executed by the game) according to the patien's needs. We believe the quality of the theraphy is related to the subject's emotional state. The long term goal is to keep the user into a specific emotional state in order to maximize the theraphy efficacy.
Project phases:
These projects allow to experiment with biological-data acquisition tools, robots and videogame design. The project consists on the realization of one or more phases depending on the difficulty/cfu to be achieved and to the competences of the candidate(s) | |
| Tutor: | Cristiano Alessandro (alessandro-AT-elet-DOT-polimi-DOT-it), Simone Tognetti (togetti-AT-elet-DOT-polimi-DOT-it) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1 to 3 | |
| CFU: | 2.5 to 20 |
| Title: | Driving companions | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | The goal of this activity is to develop an application that is able to capture your emotional state (stress, attention level .. ) while driving standard cars. The application will measure the driver's stress level by analizing his biological signals, which mirror the phisiological state, and could be used to give feedbacks to the driver in dangerous situations.
Project phases:
These projects allow to experiment with biological-data acquisition tools, robots and videogame design. The project consists on the realization of one or more phases depending on the difficulty/cfu to be achieved and to the competences of the candidate(s) | |
| Tutor: | Cristiano Alessandro (alessandro-AT-elet-DOT-polimi-DOT-it), Simone Tognetti (togetti-AT-elet-DOT-polimi-DOT-it) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1 to 3 | |
| CFU: | 2.5 to 20 |
Ontologies and Semantic Web
| Title: | Automatic generation of domain ontologies | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | This thesis to be developed together with Noustat S.r.l., who are developing research activities directed toward the optimization of knowledge management services, in collaboration with another company operating in this field. This project is aimed at removing the ontology building bottleneck, long and expensive activity that usually requires the direct collaboration of a domain expert. The possibility of automatic building the ontology, starting from a set of textual documents related to a specific domain, is expected to improve the ability to provide the knowledge management service, both by reducing the time-to-application, and by increasing the number of domains that can be covered. For this project, unsupervised learning methods will be applied in sequence, exploiting the topological properties of the ultra-metric spaces that emerge from the taxonomic structure of the concepts present in the texts, and associative methods will extend the concept network to lateral, non-hierarchical relationships. | |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Andrea Bonarini (email) | |
| Start: | before November 30th | |
| Number of students: | 1-2 | |
| CFU: | 20 |
Robotics
| Title: | Robot games | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | The goal of this activity is to develop an interactive game with robots using commercial devices such as the WII Mote (see the Robogames page)
Projects are available in different areas:
These projects allow to experiment with real mobile robots and real interaction devices. Parts of these projects can be considered as course projects. These projects can also be extended to cover course projects. | |
| Tutor: | Andrea Bonarini (bonarini-AT-elet-DOT-polimi-DOT-it) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1-2 | |
| CFU: | 7.5-20 |