LionHell McMillan II
| Title: | LIONHELL MCMILLAN II: RIPROGETTAZIONE DI UN ROBOT ESAPODE BIOLOGICAMENTE ISPIRATO PER AREE MORFOLOGICAMENTE INSTABILI | [[Image:|center|300px]] |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | Hexapode wheg robot | |
| Tutor: | Giuseppina Gini | |
| Start: | 01/09/2014 | |
| Number of students: | 1 | |
| CFU: | 20 |
CHANGES IN PROGRESS
LionHell McMillan II is an hexapode wheg robot. LionHell McMillan has been developed in a Master Thesis work in Robotics and Artificial Intelligence by Vittorio Lumare ( http://airlab.ws.dei.polimi.it/index.php/LionHell_McMillan )
and it has been modified and improved in a Master Thesis work in Robotics and Artificial Intelligence by Alessandro Rosina (changing the name from "LionHell McMillan" to "LionHell McMillan II").
Info about Thesis
TItle : LIONHELL MCMILLAN II: RIPROGETTAZIONE DI UN ROBOT ESAPODE BIOLOGICAMENTE ISPIRATO PER AREE MORFOLOGICAMENTE INSTABILI Robot Name: LionHell McMillan II Supervisor: Giuseppina Gini Correlator: Vittorio Lumare Author: Alessandro Rosina Area: Robotics and Artifical Intelligence Start date: 2014/09/10 End date: 2015/04/29
Control and Mobility in LionHell II
Wheg in LionHell II
The whegs are a mechanism of locomotion for robots that combine
simplicity of movement of a wheel with the ability to scale and to overcome obstacles arising from the use of the legs. The acronym derives
by the combination of words wheel and leg, and mechanically consist of a central rotary axis which are connected one or more bars
which perform the function of the legs.
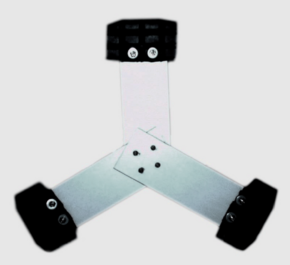
LionHell II has a total of 6 Wheg and each Wheg is composed of 3 bars arranged at 120° apart from each from the other, the ends of which is
mounted a foot slightly curved so as to ensure a secure grip on the ground. The movement of Wheg is simultaneous and each Wheg is controlled
by an independent motor that works in continuous mode, ensuring a smooth motion and robot suitable for every situation.
The Wheg that owns LionHell II is characterized by:
- a structure baseline, aluminium, guarantees the point of contact with the central hub;
- a basal structure of the foot, wood, molded according to an embodiment curve so as to adapt better to the ground and avoid jolts;
- the foam, in contact with the foot structure, reduces shocks of the robot in contact with the ground;
- rubber, in direct contact with the ground, protects the foam wear and allows the robot to move easily on any surface area;
- the symbol allows to easily identify the components of the Wheg and position of the leg in the same robot;
- the outline contour allows to understand intuitively the position with which the other members of Wheg be mounted.
Compared to the previous model, we have kept the metal rod base and the rubber that was removed from the foot, since the movement of the same LionHell would irreparably damaged the Wheg and in particular the delicate foothold.