Difference between revisions of "Master Level Course Projects"
DavidLaniado (Talk | contribs) m |
(→Computational Intelligence and Games) |
||
| (29 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Here you can find a list of project proposals for the courses of "Laboratorio di Intelligenza Artificiale e Robotica" (5 CFU for each student) and "Soft Computing" (1 CFU for each student). See [[Project Proposals]] for other kinds of projects and theses. | Here you can find a list of project proposals for the courses of "Laboratorio di Intelligenza Artificiale e Robotica" (5 CFU for each student) and "Soft Computing" (1 CFU for each student). See [[Project Proposals]] for other kinds of projects and theses. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==== BioSignal Analysis ==== | ==== BioSignal Analysis ==== | ||
| Line 108: | Line 42: | ||
|cfu=5-20 | |cfu=5-20 | ||
|image=LURCH_wheelchair.jpg}} | |image=LURCH_wheelchair.jpg}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{Project template | {{Project template | ||
| Line 281: | Line 199: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{Project template | {{Project template | ||
| − | |title= | + | |title=humanoid vision |
| − | |tutor=[[User: | + | |tutor=[[User:Giuseppina Gini|Giuseppina Gini]] ([mailto:gini%40%65%6c%65%74%2e%70%6f%6c%69%6d%69%2e%69%74 email]) |
| − | |description= | + | |description=Our goal is to develop vision capabilities for a humanoiud robot. In particular: |
| + | * NEURAL-BASED VISION SYSTEM - In this project we experiment different models of the neural structure of the visual cortex. In particular we collect couples of images with different fixation point and we reconstruct disparity, depth, shape recognition. A stereo disparity map is already available. | ||
| + | * RECOGNITION OF HAND MOTIONS - Develop a system able to recognize the hand gestures from images of people. Use this for robot interfacing. | ||
| + | * SEMANTIC MODELLING OF ACTIONS - Construct a semantic representation of actions to be matched against the data obtained from video/movements analysis. | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | |start= Anytime | |
| + | |number=1-3 | ||
| + | |cfu=2.5-15 | ||
| + | |image=vision.jpg | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | + | ==== E-Science ==== | |
| − | + | {{Project template | |
| − | + | |title=Knowledge discovery in life sciences | |
| − | * | + | |tutor=[[User:Gini Giuseppina|Gini Giuseppina]] ([mailto:gini%40%65%6c%65%74%2e%70%6f%6c%69%6d%69%2e%69%74 email]) |
| + | |description=The goal of those projects is to develop methods and applications in the broad area of life sciences applications. Basic knowledge of chemistry and biology is useful. | ||
| + | * DATA MINING FOR RULE INDUCTION - The project is about analysing large data sets to discover correlations between substructures and properties. CDK and WEKA are possible software to use. | ||
| + | * IReNNS: LEARNING FROM STRUCTURES - This project will develop IReNNS, a recurrent neural net package, and develop new applications. | ||
| + | * REC analysis in WEKA - The project is about theory and the implementation in Java of REC diagrams. A Matlab tool is available at http://www.cs.rpi.edu/~bij2/rec.html. | ||
| + | * HOW TO TEACH SCIENCE - Propose a web site to teach University students a scientific topic using active participation and virtual experimentation. | ||
| + | * CAUSAL REASONING - In this project we will develop the theory of causality proposed by Pearl and apply it to examples in biological sciences. | ||
| + | Other topics coming soon. | ||
| − | |start=Anytime | + | |start= Anytime |
| − | |number= | + | |number=2-3 |
| − | |cfu= | + | |cfu=5-20 |
| − | |image= | + | |image=life.jpg |
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Machine Learning ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{#ask: [[Category:ProjectProposal]] | ||
| + | [[PrjResArea::Machine Learning]] | ||
| + | [[PrjLevel::Ms]] | ||
| + | [[PrjType::Course]] | | ||
| + | ?PrjTitle | | ||
| + | ?PrjImage | | ||
| + | ?PrjDescription | | ||
| + | ?PrjTutor | | ||
| + | ?PrjStarts | | ||
| + | ?PrjStudMin | | ||
| + | ?PrjStudMax | | ||
| + | ?PrjCFUMin | | ||
| + | ?PrjCFUMax | | ||
| + | ?PrjResArea | | ||
| + | ?PrjResTopic | | ||
| + | format = template | | ||
| + | template = Template:ProjectProposalViz | ||
| + | }} | ||
{{Project template | {{Project template | ||
| Line 314: | Line 265: | ||
|image=keepaway.gif}} | |image=keepaway.gif}} | ||
| − | + | ==== Computational Intelligence and Games ==== | |
| − | + | {{#ask: [[Category:ProjectProposal]] | |
| − | + | [[PrjResTopic::Computational Intelligence and Games]] | |
| − | + | [[PrjLevel::Ms]] | |
| − | + | [[PrjType::Course]] | | |
| − | + | ?PrjTitle | | |
| − | + | ?PrjImage | | |
| − | + | ?PrjDescription | | |
| − | + | ?PrjTutor | | |
| − | + | ?PrjStarts | | |
| − | {{ | + | ?PrjStudMin | |
| − | + | ?PrjStudMax | | |
| − | + | ?PrjCFUMin | | |
| − | + | ?PrjCFUMax | | |
| − | | | + | ?PrjResArea | |
| − | | | + | ?PrjResTopic | |
| − | | | + | format = template | |
| − | | | + | template = Template:ProjectProposalViz |
| − | + | }} | |
| − | + | ||
| − | | | + | |
| − | | | + | |
| − | | | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | | | + | |
| − | | | + | |
| − | | | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | | | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ==== Social Software and Semantic Web ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
{{#ask: [[Category:ProjectProposal]] | {{#ask: [[Category:ProjectProposal]] | ||
| − | [[PrjResArea:: | + | [[PrjLevel::Bs]] |
| + | [[PrjType::Course]] | ||
| + | [[PrjResArea::Social Software and Semantic Web]] | | ||
?PrjTitle | | ?PrjTitle | | ||
?PrjImage | | ?PrjImage | | ||
| Line 381: | Line 312: | ||
==== Robotics ==== | ==== Robotics ==== | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{#ask: [[Category:ProjectProposal]] |
| − | + | [[PrjResArea::Robotics]] | |
| − | + | [[PrjLevel::Ms]] | |
| − | + | [[PrjType::Course]] | | |
| − | + | ?PrjTitle | | |
| − | + | ?PrjImage | | |
| − | + | ?PrjDescription | | |
| − | + | ?PrjTutor | | |
| − | + | ?PrjStarts | | |
| − | + | ?PrjStudMin | | |
| − | + | ?PrjStudMax | | |
| − | + | ?PrjCFUMin | | |
| − | + | ?PrjCFUMax | | |
| − | | | + | ?PrjResArea | |
| − | | | + | ?PrjResTopic | |
| − | | | + | format = template | |
| − | | | + | template = Template:ProjectProposalViz |
| − | + | }} | |
| − | + | ||
| − | | | + | |
| − | | | + | |
| − | | | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | | | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| Line 459: | Line 373: | ||
|cfu=5-20 | |cfu=5-20 | ||
|image=KC_jc_third.jpg}} | |image=KC_jc_third.jpg}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{Project template | ||
| + | |title=Humanoid robotics | ||
| + | |tutor=Giuseppina Gini(gini-AT-elet-DOT-polimi-DOT-it) | ||
| + | |description=this project is about developing various functions of humanoids, in particular related to sensing and cognition for manipulation. Possible specific projects are: | ||
| + | * BIOINSPIRED ROBOT HEAD FOR VISION - design and build a robot head able to host 2 cameras with 2dof of freedom each to create a human-like vision system. The movements can be obtained using 4 McKibben actuators for each camera, or electric actuators. | ||
| + | * NEW HARDWARE FOR MAXIMUMOne - the humanoid robot is moved by more than 20 actuators and needs input from all of them. The new architecture FPGA based will move the arm and the head. | ||
| + | * SIMULATOR OF HUMANOID ROBOT - complete the simulator of MaximumOne with all the dof. The simulator will use the same Matlab algorithms of the controller. | ||
| + | * INTEGRATING MANIPULATION AND VISION ON MAXIMUMOne - develop a natural vision system that uses the neck and the eyes movements to follow objects and to concentrate on grasping targets. The integration can be done in matlab/Simulink and integrated in the MaximumOne model. | ||
| + | * MANIPULATION ONTOLOGIES - develop an ontology approach to find the right way to grasp an object , considering both the object and the hand characteristics. | ||
| + | * PATH PLANNING AND COLLISION AVOIDANCE IN OOPS - Randomized path planning is a strategy to produce paths for complex devices. An open source project (OOPS) is available; the project is about integrating path planning with a robot simulator. | ||
| + | |||
| + | All the projects can be turned into a thesis. | ||
| + | |start=Anytime | ||
| + | |number=4-6 | ||
| + | |cfu=5-20 | ||
| + | |image=maximum.jpg}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{Project template | ||
| + | |title=Legged locomotion | ||
| + | |tutor=[[User:Giuseppina Gini|Giuseppina Gini]] ([mailto:gini%40%65%6c%65%74%2e%70%6f%6c%69%6d%69%2e%69%74 email]) | ||
| + | |description= The proposed projects in the area of walking robots will improve the performances of on-going systems. | ||
| + | * KINEMATIC/DYNAMIC MODEL OF WARUGADAR - develop a complete kinematic analysis of a quadruped robot, useful for planning the foot position on uneven terrains. The dynamic model will be useful for learning different gaits. | ||
| + | * GAIT GENERATION AND CONTROL FOR WARUGADAR - Study Central Pattern Generation, develop a CPG implementation in Matlab or Python. Adapt the method to a quadruped robot (Warugadar). | ||
| + | * ROBO FISH - Continue the development of hardware and software for the robotic fish Zoidberg2, and study a fish colony. | ||
| + | * EMBOT WALKING - complete the robot with 4 wheels used as feet. Control it and experiment. | ||
| + | * ROBOTIC EXPERIMENTS WITH BIOLOID - using Bioloid experiments hw and gaits, develop software for the humanoid challenges at ICRA2010. | ||
| + | |||
| + | All the projects can be turned into a thesis. | ||
| + | |start=Anytime | ||
| + | |number=2-5 | ||
| + | |cfu=5-20 | ||
| + | |image=leg.jpg}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Project template | ||
| + | |title=Robotic prosthesis | ||
| + | |tutor=[[User:Giuseppina Gini|Giuseppina Gini]] ([mailto:gini%40%65%6c%65%74%2e%70%6f%6c%69%6d%69%2e%69%74 email]) | ||
| + | |description= The proposed projects in the development of an active hand prosthesis, novel in architecture since it considers anso the wrist. THe user interface is based on EMG signals. | ||
| + | * ADVANCED EMG ANALYSIS - To develop prosthesis and therapeutic tools we need to analyze EMG signals according to position, velocity, force. Starting from signal acquisition develop in Matlab a model for force and velocity control. | ||
| + | * HAND PROSTHESIS DESIGN - Define a virtual model of the hand prosthesis (actuation and sensors) and develop a controller based on multi-class classification of electro-myographic signals. | ||
| + | |||
| + | All the projects can be turned into a thesis. | ||
| + | |start=Anytime | ||
| + | |number=2-3 | ||
| + | |cfu=5-20 | ||
| + | |image=hand.jpg}} | ||
<!--==== Soft Computing ====--> | <!--==== Soft Computing ====--> | ||
Latest revision as of 19:53, 29 October 2009
Here you can find a list of project proposals for the courses of "Laboratorio di Intelligenza Artificiale e Robotica" (5 CFU for each student) and "Soft Computing" (1 CFU for each student). See Project Proposals for other kinds of projects and theses.
Contents
BioSignal Analysis
| Title: | Human-computer interaction via voice recognition system | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | We want develop a system to allow a voice interaction between the user and the wheelchair.
This project consists in develop one of the solutions proposed in literature and extended the LURCH software to include this kind of interface.
References:
| |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Davide Migliore (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1-2 | |
| CFU: | 2.5-10 |
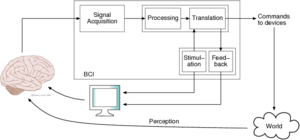
Brain-Computer Interface
| Title: | Driving an autonomous wheelchair with a P300-based BCI | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | This project pulls together different Airlab projects with the aim to drive an autonomous wheelchair (LURCH) with a BCI, through the development of key software modules. Depending on the effort the student is willing to put into it, the project can grow to a full experimental thesis.
| |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Bernardo Dal Seno (email) | |
| Start: | November 2008 | |
| Number of students: | 1 | |
| CFU: | 5-20 |
| Title: | Reproduction of an algorithm for the recognition of error potentials | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | Error potentials (ErrPs) are event-related potentials present in the EEG (electroencephalogram) when a subject makes a mistake or when the machine a subject is interacting with works in an expected way. They could be used in the BCI field to improve the performance of a BCI by automatically detecting classification errors.
The project aims at reproducing algorithms for ErrP detection from the literature.
| |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Bernardo Dal Seno (email) | |
| Start: | This project has already been assigned | |
| Number of students: | 1 | |
| CFU: | 5-15 |
Computer Vision and Image Analysis
| Title: | Environment Monitoring | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | The goal of this project is to develop a video surveillance system to track in 3D vehicles or people.
The idea is to use one or more calibrated camera to estimate the position and the trajectories of the moving objects in the scene. The skills required for this project are:
The project can be turned into a thesis extending the algorithm for a generic outdoor environment. | |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Davide Migliore (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 2-3 | |
| CFU: | 10-15 |
| Title: | Visual Merchandising | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | The goal of this project is to develop algorithms to count the number of products on the shelves of a market.
The idea is to use a calibrated camera to recognize the shelves, estimate the scale and improve the image quality. The skills required for this project are:
| |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Davide Migliore (email) | |
| Start: | As soon as possible | |
| Number of students: | 2-3 | |
| CFU: | 2.5-15 |
| Title: | Analysis of patch recognition algorithms | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | Extract distinctive features from images is very important in computer vision application.
It can be used in algorithms for tasks like matching different views of an object or scene (e.g. for stereo vision) and object recognition. The aim of this work is to integrate in an existent framework the existing solution proposed in literature. Skills
References: | |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Davide Migliore (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 2-3 | |
| CFU: | 2.5-15 |
| Title: | Catadioptric MonoSLAM | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | The goal of this work is to investigate a SLAM solutions based on catadioptric camera, integrating the solution presented in literature into an existing frameword.
Improvements could be the basis for a tesi. Skills
References: | |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Davide Migliore (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 2-3 | |
| CFU: | 2.5-15 |
| Title: | Trinocular Vision System (SUGR) | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | A Trinocular Vision System is a device composed by three cameras that allows to measure 3D data (in this case segments) directly from images.
The aim of this tesina/project is to implement a trinocular algorithm based on SUGR, a library for Uncertain Projective Geometry. Skills
| |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Davide Migliore (email) | |
| Start: | As soon as possible | |
| Number of students: | 2-3 | |
| CFU: | 2.5-15 |
| Title: | GIFT and features extraction and description | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | The idea is to improve and optimize the solution proposed by Campari et al. in their paper, who propose to estimate invariant descriptor using geodesic features descriptor based on color information.
Skills
| |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Davide Migliore (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1-3 | |
| CFU: | 10-20 |
| Title: | Multimedia Indexing Framework | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | The goal of this project is to develop a framework for multimedia indexing.
The idea is create an images database indexer that allows to make query using images or strings. Skills
References: | |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Davide Migliore (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1-3 | |
| CFU: | 2.5-15 |
| Title: | humanoid vision | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | Our goal is to develop vision capabilities for a humanoiud robot. In particular:
| |
| Tutor: | Giuseppina Gini (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1-3 | |
| CFU: | 2.5-15 |
E-Science
| Title: | Knowledge discovery in life sciences | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | The goal of those projects is to develop methods and applications in the broad area of life sciences applications. Basic knowledge of chemistry and biology is useful.
Other topics coming soon. | |
| Tutor: | Gini Giuseppina (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 2-3 | |
| CFU: | 5-20 |
Machine Learning
| Wiki Page: | Combinatorial optimization based on stochastic relaxation | |
| Title: | Combinatorial optimization based on stochastic relaxation | |
| Description: | The project will focus on the study, implementation, comparison and
analysis of different algorithms for the optimization of pseudo-Boolean functions, i.e., functions defined over binary variables with values in R. These functions have been studied a lot in the mathematical programming literature, and different algorithms have been proposed (1). More recently, the same problems have been faced in evolutionary computations, with the use of genetic algorithms, and in particular estimation of distribution algorithms (2,3). Estimation of distribution algorithms are a recent meta-heuristic, where classical crossover and mutation operators used in genetic algorithms are replaced with operators that come from statistics, such as sampling and estimation. The focus will be on the implementation of a new algorithm able to combine different approaches (estimation and sampling, from one side, and exploitation of prior knowledge about the structure of problem, on the other), together with the comparison of the results with existing techniques that historically appear in different (and often separated) communities. Good coding (C/C++) abilities are required. Since the approach will be based on statistical models, the student is supposed to be comfortable with notions that come from probability and statistics courses. The project could require some extra effort in order to build and consolidate some background in math, especially in Bayesian statistics and MCMC techniques, such as Gibbs and Metropolis samplers (4). The project can be extended to master thesis, according to interesting and novel directions of research that will emerge in the first part of the work. Possible ideas may concern the proposal of new algorithms able to learn existing dependencies among the variables in the function to be optimized, and exploit them in order to increase the probability to converge to the global optimum. Picture taken from http://www.ra.cs.uni-tuebingen.de/ Bibliography
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Machine Learning | |
| Research Topic: | Information Geometry, Stochastic Optimization |
| Wiki Page: | Combining Estimation of Distribution Algorithms and other Evolutionary techniques for combinatorial optimization | |
| Title: | Combining Estimation of Distribution Algorithms and other Evolutionary techniques for combinatorial optimization | |
| Description: | The project will focus on the study, implementation, comparison and analysis of different algorithms for combinatorial optimization using techniques and algorithms proposed in Evolutionary Computation. In particular we are interested in the study of Estimation of Distribution Algorithms (1,2,3,4), a recent meta-heuristic, often presented as an evolution of Genetic Algorithms, where classical crossover and mutation operators, used in genetic algorithms, are replaced with operators that come from statistics, such as sampling and
estimation. The focus will be on the implementation of new hybrid algorithms able to combine estimation of distribution algorithms with different approaches available in the evolutionary computation literature, such as genetic algorithms and evolutionary strategies, together with other local search techniques. Good coding (C/C++) abilities are required. Some background in combinatorial optimization form the "Fondamenti di Ricerca Operativa" is desirable. The project could require some effort in order to build and consolidate some background in MCMC techniques, such as Gibbs and Metropolis samplers (4). The project could be extended to master thesis, according to interesting and novel directions of research that will emerge in the first part of the work. Computer vision provides a large number of optimization problems, such as new-view synthesis, image segmentation, panorama stitching and texture restoration, among the others, (6). One common approach in this context is based on the use of binary Markov Random Fields and on the formalization of the optimization problem as the minimum of an energy function expressed as a square-free polynomial, (5). We are interested in the proposal, comparison and evaluation of different Estimation of Distribution Algorithms for solving real world problems that appear in computer vision. Pictures taken from http://www.genetic-programming.org and (6) Bibliography
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 10 | |
| Research Area: | Machine Learning | |
| Research Topic: | Evolutionary Computation, Stochastic Optimization |
| Wiki Page: | Information geometry and machine learning | |
| Title: | Information geometry and machine learning | |
| Description: | In machine learning, we often introduce probabilistic models to handle uncertainty in the data, and most of the times due to the computational cost, we end up selecting (a priori, or even at run time) a subset of all possible statistical models for the variables that appear in the problem. From a geometrical point of view, we work with a subset (of points) of all possible statistical models, and the choice of the fittest model in out subset can be interpreted as a the point (distribution) minimizing some distance or divergence function w.r.t. the true distribution from which the observed data are sampled. From this perspective, for instance, estimation procedures can be considered as projections on the statistical model and other statistical properties of the model can be understood in geometrical terms. Information Geometry (1,2) can be described as the study of statistical properties of families of probability distributions, i.e., statistical models, by means of differential and Riemannian geometry.
Information Geometry has been recently applied in different fields, both to provide a geometrical interpretation of existing algorithms, and more recently, in some contexts, to propose new techniques to generalize or improve existing approaches. Once the student is familiar with the theory of Information Geometry, the aim of the project is to apply these notions to existing machine learning algorithms. Possible ideas are the study of a particular model from the point of view of Information Geometry, for example as Hidden Markov Models, Dynamic Bayesian Networks, or Gaussian Processes, to understand if Information Geometry can give useful insights with such models. Other possible direction of research include the use of notions and ideas from Information Geometry, such as the mixed parametrization based on natural and expectation parameters (3) and/or families of divergence functions (2), in order to study model selection from a geometric perspective. For example by exploiting projections and other geometric quantities with "statistical meaning" in a statistical manifold in order to chose/build the model to use for inference purposes. Since the project has a theoretical flavor, mathematical inclined students are encouraged to apply. The project requires some extra effort in order to build and consolidate some background in math, partially in differential geometry, and especially in probability and statistics. Bibliography
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 20 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Machine Learning | |
| Research Topic: | Information Geometry |
| Wiki Page: | LARS and LASSO in non Euclidean Spaces | |
| Title: | LARS and LASSO in non Euclidean Spaces | |
| Description: | LASSO (1) and more recently LARS (2) are two algorithms proposed for linear regression tasks. In particular LASSO solves a least-squares (quadratic) optimization problem with a constrain that limits the sum of the absolute value of the coefficients of the regression, while LARS can be considered as a generalization of LASSO, that provides a more computational efficient way to obtain the solution of the regression problem simultaneously for all values of the constraint introduced by LASSO.
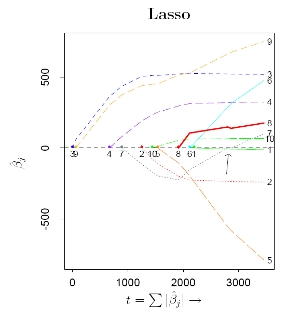
One of the common hypothesis in regression analysis is that the noise introduced in order to model the linear relationship between regressors and dependent variable has a Gaussian distribution. A generalization of this hypothesis leads to a more general framework, where the geometry of the regression task is no more Euclidean. In this context different estimation criteria, such as maximum likelihood estimation and other canonical divergence functions do not coincide anymore. The target of the project is to compare the different solutions associated to different criteria, for example in terms of robustness, and propose generalization of LASSO and LARS in non Euclidean contexts. The project will focus on the understanding of the problem and on the implementation of different algorithms, so (C/C++ or Matlab or R) coding will be required. Since the project has also a theoretical flavor, mathematical inclined students are encouraged to apply. The project may require some extra effort in order to build and consolidate some background in math, especially in probability and statistics. Picture taken from (2) Bibliography
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 20 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Machine Learning | |
| Research Topic: | Informtion Geometry |
| Wiki Page: | Statistical inference for phylogenetic trees | |
| Title: | Statistical inference for phylogenetic trees | |
| Description: | The project will focus on the study, implementation, comparison, and analysis of different statistical inference techniques for phylogenetic trees. Phylogenetic trees (1, 2, 3) are evolutionary trees used to represent the relationships between different species with a common ancestor. Typical inference tasks concern the construction of a tree starting from DNA sequences, involving both the choice of the topology of the tree (i.e., model selection) and the values of the parameters (i.e., model fitting). The focus will be a probabilistic description of the tree, given by the introduction of stochastic
variables associated to both internal nodes and leaves of the tree. The project will focus on the understanding of the problem and on the implementation of different algorithms, so (C/C++ or Matlab or R) coding will be required. Since the approach will be based on statistical models, the student is supposed to be comfortable with notions that come from probability and statistics courses. The project is thought to be extended to master thesis, according to interesting and novel directions of research that will emerge in the first part of the work. Possible ideas may concern the proposal and implementation of new algorithms, based on recent approaches to phylogenetic inference available in the literature, as in (3) and (4). In this case the thesis requires some extra effort in order to build and consolidate some background in math in oder to understand some recent literature, especially in (mathematical) statistics and, for example, in the emerging field of algebraic statistics (5). Other possible novel applications of phylogenetic trees have been proposed in contexts different from biology, as in (6). Malware (malicious software) is software designed to infiltrate a computer without the owner's informed consent. Often malwares are related to previous programs thought evolutionary relationships, i.e., new malwares appear as small mutations of previous softwares. We are interested in the use of techniques from phylogenetic trees to create a taxonomy of real world malwares. Picture taken from http://www.tolweb.org/tree/ and http://www.blogscienze.com Bibliography
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Machine Learning | |
| Research Topic: | Information Geometry, Stocastic Optimization, Evolutionary Computation |
| Title: | Reinforcement Learning Competition | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | This project has the goal of participating to (and possibly winning ;)) the 2009 Reinforcement Learning competition. To have an idea of what participate to such a competition means you can have a look at the website of the 2008 RL competition.
The problems that will be proposed are still unknown. As soon as the domains will be published, the work will start by analyzing their main characteristics and, then we will identify which RL algorithms are most suited for solving such problems. After an implementation phase, the project will required a long experimental period to tune the parameters of the learning algorithms in order to improve the performance as much as possible. | |
| Tutor: | Marcello Restelli (restelli-AT-elet-DOT-polimi-DOT-it) | |
| Start: | January, 2009 | |
| Number of students: | 2-4 | |
| CFU: | 10-20 |
Computational Intelligence and Games
| Wiki Page: | AI in Racing Games | |
| Title: | AI in Racing Games | |
| Description: | This project is focused on TORCS, a state-of-the-art open source racing simulator. From one hand, TORCS represents an ideal bechmark to study Computational Intelligence techniques. On the other hand, Computational Intelligence techniques could be used to improve the game experience in this kind of games. Several projects and theses are available on this topic, please contact us for additional information.
References:
| |
| Tutor: | [[DanieleLoiacono | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Computational Intelligence and Games | |
| Research Topic: | Computational Intelligence and Games |
| Wiki Page: | Automatic Content Generation in Computer Games | |
| Title: | Automatic Content Generation in Computer Games | |
| Description: | The generation of customized game content for each player is an attractive direction to improve the game experience in the next-generation computer games. In this scenario, Machine Learning could play an important role to provide automatically such customized game content. Several projects and theses are available on this topic, please contact us for additional information.
Picture taken from http://gar.eecs.ucf.edu/
| |
| Tutor: | [[DanieleLoiacono | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Computational Intelligence and Games | |
| Research Topic: | Computational Intelligence and Games |
| Wiki Page: | Data Mining in Computer Games | |
| Title: | Data Mining in Computer Games | |
| Description: | Today a lot of data can be extracted from popular games. The analysis of such data allow to discover a lot of interesting information about players, the game and the interaction between the game and different type of players.
Several theses and projects are available on this topic and involve different games: TORCS, Unreal Tournament and Quake Live. Please contact us for additional information.
| |
| Tutor: | [[DanieleLoiacono | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Computational Intelligence and Games | |
| Research Topic: | Computational Intelligence and Games |
| Wiki Page: | Human-Like AI in Games | |
| Title: | Human-Like AI in Games | |
| Description: | Developing a human-like AI is a challenging and fascinating problem from the point of view of the Artificial Intelligence research. At the same time, it is also a significative prolem for the computer games development: playing against humans is generally more exciting than playing against computers.
Our projects and theses on this topic involve two different games: Unreal Tournament 2004 and TORCS. Please contact us for additional information.
| |
| Tutor: | [[DanieleLoiacono | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Computational Intelligence and Games | |
| Research Topic: | Computational Intelligence and Games |
Social Software and Semantic Web
| Wiki Page: | A firefox extension for semantic annotations | |
| Title: | A Firefox extension for semantic annotations | |
| Description: | Aim of this project is to develop a Firefox extension, to allow a community of users to annotate resources on the Web using a shared RDF vocabulary.
While browsing the Web, a user should be able to visualize the annotations relative to the page they are visiting, and to add new annotations as well. | |
| Tutor: | [[DavidLaniado | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | ||
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Social Software and Semantic Web | |
| Research Topic: | Semantic Annotations |
| Wiki Page: | Annotation aggregators from social applications | |
| Title: | Annotation aggregators from social applications | |
| Description: | Annotations are metadata published about a resource, such as tags in del.icio.us, comments on stumbleupon.com, or twines on Twine.com. One of the main problems of these annotations is that they are not expressed in a standard format: thus, any tool trying to aggregate information from these sources should be able to access each one of them in a different way.
The purpose of this project is to develop translation tools for different social annotation systems, collect their data in a common format (expressed using an ontology), and show them through a unique user interface, able to display different annotations (i.e. geo coordinates, dates, tags, etc.) in different ways. Moreover, tests and evaluations should be performed on this aggregator to show how efficient the queries are when performed on-the-fly or from an intermediate knowledge base. | |
| Tutor: | [[DavideEynard | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | ||
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Social Software and Semantic Web | |
| Research Topic: | Semantic Annotations |
| Wiki Page: | Extending a search engine with semantic information | |
| Title: | Extending a search engine with semantic information | |
| Description: | We are used to keyword-based search engines, where only documents matching the exact words in the query are retrieved. In a traditional search engine, if you submit the query "a dinosaur in a university in Lombardy" you won't probably find a document containing the phrase "a velociraptor in Politecnico di Milano", even though it's more or less what you were looking for.
Aim of this project is to expand a traditional search engine with semantic information, so that also documents containing words related to the ones in the query can be retrieved. Existing thesauri and ontologies can be used, as well as more dynamic and collaborative sources of knowledge such as user tags and wikipedia pages and categories. Starting points for this work can be the projects "SeQuEx - Semantic Query Expansion" and "Enriching search results with semantic metadata". | |
| Tutor: | [[DavidLaniado | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | ||
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Social Software and Semantic Web | |
| Research Topic: | Semantic Search |
| Wiki Page: | Facebook automatic list suggestion | |
| Title: | Facebook Automatic List Suggestion | |
| Description: | In Facebook each user can create lists of friends (for example: "high school","university","tennis") to better filter information and manage privacy.
Goal of this project is to develop a Facebook application to analyze a user's network of friends and automatically detect groups to suggest lists. | |
| Tutor: | [[DavidLaniado | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | ||
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 10 | |
| Research Area: | Social Software and Semantic Web | |
| Research Topic: | Social Network Analysis |
| Wiki Page: | Mining wikipedia categories | |
| Title: | Wikipedia category map | |
| Description: | Wikipedia articles are organized in a hierarchy of categories, manually assigned by users. This process can be considered a huge effort for the collective categorization of human knowledge; the result is a wide and disordered graph which can provide precious information for a variety of applications (natural language processing, information retrieval, ontology building...).
In the project "Wikipedia Category Map" a tool has been developed to extract the graph of Wikipedia categories, to store it in RDF format and to interactively visualize and explore it. Aim of this project is to analyze the resulting graph for the extraction of semantic relationships; for example it is possible to define metrics of distance between topics in the graph, which can be useful for various purposes in information retrieval. | |
| Tutor: | [[DavidLaniado | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 7 July 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Social Software and Semantic Web | |
| Research Topic: | Semantic Tagging |
| Wiki Page: | Social Network Data Extraction from Online Communities | |
| Title: | Social Network Data Extraction From Online Communities | |
| Description: | With the growth of the Web and the emergence of online communities, a huge amount of data regarding social relationships is now available, that was unthinkable until a few years ago. The network of connections may unveil precious information about communities structures and dynamics and the spreading of information in the Web.
Aim of this project is to design and develop a software tool to extract this kind of information from a single social network platform (decided by the student). It may be required also some kind of analysis or visual representation of the collected data. | |
| Tutor: | [[DavidLaniado | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | ||
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Social Software and Semantic Web | |
| Research Topic: | Social Network Analysis |
| Wiki Page: | Use case design and implementation for semantic annotations | |
| Title: | Use case design and implementation for semantic annotation | |
| Description: | Semantic annotations offer a variety of possibilities to enhance the user experience while browsing the Web. Aim of this project is to propose one scenario in which their usefulness is exploited for a specific community of users. In detail the project requires to design a simple ontology which describes some kind of domain to annotate resources on the Web and implement an interface to query it and insert assertions inside a semantic store (through SPARQL).
One possible example is the annotation of mp3 files available on the Web. They can be classified in genres or associated to datatype properties, such as rating, title, length and release date... also exploiting data already available in http://musicbrainz.org/ | |
| Tutor: | [[DavideEynard | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | ||
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 10 | |
| Research Area: | Social Software and Semantic Web | |
| Research Topic: | Semantic Annotations |
| Wiki Page: | Wikipedia Page Social Network | |
| Title: | Wikipedia Page Social Network | |
| Description: | Goal of this project is to study the social network of Wikipedia pages, where two pages are connected if they share at least one main contributor. This social network can be studied to reveal interesting information; for example, it is possible to extract clusters of pages which apparently have nothing in common. A metric of distance between pages in the network can be defined, and compared with other metrics, such as the distance in the category tree or in the hyperlink graph. | |
| Tutor: | [[DavidLaniado | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | ||
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Social Software and Semantic Web | |
| Research Topic: | Social Network Analysis |
Robotics
| Wiki Page: | BringMeHome | |
| Title: | BringMeHome | |
| Description: | ||
| Tutor: | [[AndreaBonarini | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 30 March 2013 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 2 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | E-2? - A robot for exhibitions |
| Wiki Page: | CAN Bus bootloader for STM32 microcontrollers | |
| Title: | CAN Bus bootloader for STM32 microcontrollers | |
| Description: | JOINT PROJECT with the Embedded Systems group (contact: Patrick Bellasi http://home.dei.polimi.it/bellasi/)
In order to speed up the development and the maintenance of embedded applications, a way to update the firmware on a microcontroller without the need of connecting cables or programmers can be very handy. We are developing a framework for rapid prototyping of low-cost robots, with smart devices that exchange data on a CAN bus network. The CAN bus bootloader is one of the components we need for this project, enabling remote firmware upgrades of all the devices connected to the CAN network. This project aims to develop a CAN bus bootloader for STM32 ARM Cortex-M3 microcontrollers, and eventually for other architectures. | |
| Tutor: | [[AndreaBonarini | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 March 2012 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 2 - 5 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | Robot development |
| Wiki Page: | Cognitive SLAM | |
| Title: | Cognitive SLAM | |
| Description: | We have developed a system that is able to detect, recognize and track objects in an image taken from a low cost robot equipped with a IMU and a low cost camera. The system is capable to detect and recognize objects using a user defined fuzzy tree classifier. However the system performance is heavily dependent on high level feature extraction, such as geometric features. The problem is non trivial due to noisy low cost camera and changes in the light conditions. The aim of this project is to improve the feature extraction and description process, both in performance and quality, possible adding a more complete description or others type of features. The long term aim of the research is to have an autonomuos robot capable to create a semantic map of the envirorment, localize himself , make inference on the map, navigate into the envirorment using the objects as landmarks.
No special skills are required, except basic c and object oriented programming. | |
| Tutor: | [[AndreaBonarini | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 January 2015 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | SLAM, Feature Extraction |
| Wiki Page: | Designing Living Objects | |
| Title: | Designing Living Objects | |
| Description: | The aim of this activity is to investigate how one or more objects in an antropic environment (home, office, hospital) can be designed and implemented to have a character and to move, having nice interactions with people. The work to be done concerns the analysis, definition, design and implementation of at least one of these objects. | |
| Tutor: | [[AndreaBonarini | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 15 October 2017 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | Living Objects |
| Wiki Page: | Electromagnetic kicker for middle-size RoboCup soccer robots | |
| Title: | Electromagnetic kicker for middle-size RoboCup soccer robots | |
| Description: | The Milan RoboCup Team, a team of soccer robots that play in the Middle Size league of RoboCup (1) employs as kicker an electromagnetic device entirely designed within the AIRLab with external collaborations such as the Energetic department at Politecnico di Milano and the Electronics section at DEI. Basically, the device consists of a solenoid, a capacitor and a PIC-based board that controls (through an external integrated circuit) the charge of the capacitor at 400V (using the 24V batteries of the robot) and the generation of the magnetic field in the solenoid. The magnetic field accelerates a metallic cylinder that hits the soccer ball.
The aim of the project is to design, implement, test, and evaluate a new version of the device. While the charge phase, implemented by an ad-hoc IC controlled by the PIC, is quite efficient, some work has to be done in order to design a new solenoid and improve the way the PIC implements a sort of modulation of strength of the shoot, in order to implement small passages between robots. The final purpose is to improve the efficiency of the system, with the aim of minimize the energy consumed and maximize the energy transmitted to the ball, in order to obtain more powerful shots. The first part of the project is focused on some theoretical aspects in order to understand the current design and evaluate how to improve it, while the second phase will be focused on the implementation and test of a new prototype of the kicking device. Experience with PIC-based systems is a plus, but not required, while some experience with electronics circuits is highly recommended. Students are supposed to work in the lab following a set of safety guidelines and rules with circuits at 400V, with 10A pick current during charge phase, and even more during shots. Student from electronics engineering are really welcomed to choose this project. | |
| Tutor: | [[LuigiMalago | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 5 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | Milan Robocup Team |
| Wiki Page: | Embedded registers view plug-in for Eclipse | |
| Title: | Embedded registers view plug-in for Eclipse | |
| Description: | JOINT PROJECT with the Embedded Systems group (contact: Patrick Bellasi http://home.dei.polimi.it/bellasi/)
When developing embedded applications it is frequently needed to look at *hardware register content* in order to *debug the code*. All commercial development suites offer register views that show their contents as well as the meaning of each bit. Open source development solutions currently lack this feature, meaning that you have to look to the correct memory location and map the content to the corresponding register bits manually. This seems to be one of the most limiting issues when developing embedded application using open source solutions. This project aims to fill this gap, developing an Eclipse plug-in that shows the register contents in a tree viewer, like most commercial suites do. | |
| Tutor: | [[AndreaBonarini | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 30 May 2011 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 2 - 5 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | Robot development |
| Wiki Page: | Odometric system for robots based on laser mice | |
| Title: | Odometric system for robots based on laser mice | |
| Description: | We developed an odometric system for robots by combining the reading of several laser mice. The system consists of a master PIC-based board and several slave boards where the sensors employed in optical mice are located. The readings are collected on the PIC and sent on the serial port to a PC which elaborates and combines the x and y readings in order to obtain a x,y,theta estimation of the movement of the robot.
The aim of the project is first to improve the current design of the PIC-based board, and realize a new working prototype, and then to implement and evaluate different algorithms able to estimate more precisely the x,y and theta odometric data from the mice readings. Experience with PIC-based systems and some experience with electronics circuits is a plus. Students are supposed to redesign the electronic board, improve the firmware of the PIC, and work on the algorithm that estimates the robot position on the PC. It would be also interesting to evaluate the possibility to embed the optimization and estimation algorithms in the firmware of the PIC in order to produce a stand-alone device. Ask the tutors of the project for extra material, such as data-sheets and other documentation. | |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | Robot development |
| Wiki Page: | R2P IMU firmware development | |
| Title: | Embedded Inertial Measurement Unit for Unmanned Aerial Vehihcles | |
| Description: | We have developed the electronics of an Inertial Measurement Unit based on an ARM microcontroller to be integrated on an autonomous embedded aerial platform. The IMU has already some attitude heading reference system (AHRS) code implemented, but we are interested in:
Material
Expected outcome:
Required skills or skills to be acquired:
| |
| Tutor: | [[AndreaBonarini | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 January 2015 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 2 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | Robot development |
| Wiki Page: | Robot Games | |
| Title: | Robot Games | |
| Description: | Projects may include the design of an interactive game on an existing or a new robot, and its evaluation. These projects allow to experiment with real mobile robots and interaction devices. Some games may be designed for disabled children. The project can be considered a MS thesis if it can produce a new game and, possibly, a new robot, and includes adapting the behavior of the robot to the player. | |
| Tutor: | [[AndreaBonarini | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | ||
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 2 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | Robogames |
| Wiki Page: | Scripting language on embedded platforms | |
| Title: | Scripting language on embedded platforms | |
| Description: | JOINT PROJECT with the Embedded Systems group (contact: Patrick Bellasi http://home.dei.polimi.it/bellasi/)
When developing embedded applications it is common the need to test some algorithm in some fast way, without to re-program the whole firmware every time. PAWN (http://www.compuphase.com/pawn/) is a *simple and lightweight scripting language with a C-like syntax*. Execution speed, stability, simplicity and a small footprint were essential design criteria for both the language and the abstract machine, making PAWN suitable for embedded applications. This project aims to port the abstract machine to ARM Cortex-M3 microcontrollers, add a set of functions to interface with the underlying hardware peripherals and then to embed it as ChibiOS/RT (http://www.chibios.org) thread. | |
| Tutor: | [[AndreaBonarini | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 30 May 2011 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 2 - 5 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | Robot development |
| Wiki Page: | Soccer Robots | |
| Title: | Soccer Robots | |
| Description: | Projects are available in different areas:
The project can be turned into a thesis by facing different problems in depth. | |
| Tutor: | [[MarcelloRestelli | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 January 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | Robot development |
| Wiki Page: | Stability and motion control of a balancing robot | |
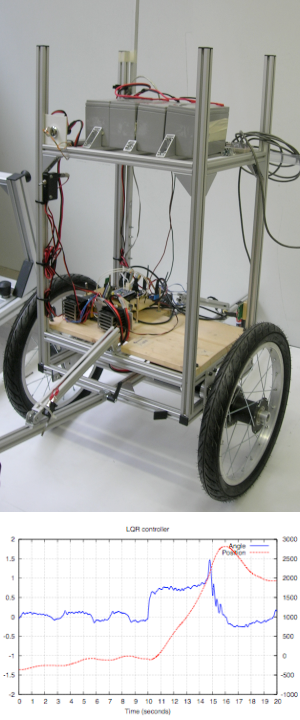
| Title: | Stability and motion control of a balancing robot | |
| Description: | This project is focused on the control of both stability and motion of TiltOne, a balancing robot.
TiltOne is a robot with only two wheels that can stand in vertical position following an unstable equilibrium point. The control is applied by commanding an amount of torque to the wheels, allowing the robot to mantain it's gravity center vertical aligned to the wheel axis. The aim of the project proposal is to implement and compare different control solutions, based on classical approach (as PID and LQR control) and Machine Learning approach (as Reinforcement Learning control policies), that allow the robot to move following a given trajectory at a given speed. | |
| Tutor: | [[AndreaBonarini | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 March 2010 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | Robot development |
| Title: | Calibration of IMU-camera system | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | This work is about the problem to calibrate a system composed by an XSense
Inertial Measurement Unit and a Fire-i Camera. The pro ject will be focus on the problem to estimate both unknown rotation between the two devices and the extrinsic/intrinsic parameters of the camera. This algorithm allows to use the system for SLAM or robotics applications, like a wereable device for autonomous navigation or augmented reality.
| |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Davide Migliore (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1 | |
| CFU: | 5-20 |
| Title: | MonoSLAM system implementation | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | The aim of this proposal is to investigate the different monocamera SLAM solution proposed in literature.
After a deepen bibliography research, the work will be focused on developing one of these algorithms into an existing framework and, only for tesi option, investigate possible improvements. The algorithms interested are based on [14]:
| |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Davide Migliore (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1-2 | |
| CFU: | 5-20 |
| Title: | Humanoid robotics | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | this project is about developing various functions of humanoids, in particular related to sensing and cognition for manipulation. Possible specific projects are:
All the projects can be turned into a thesis. | |
| Tutor: | Giuseppina Gini(gini-AT-elet-DOT-polimi-DOT-it) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 4-6 | |
| CFU: | 5-20 |
| Title: | Legged locomotion | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | The proposed projects in the area of walking robots will improve the performances of on-going systems.
All the projects can be turned into a thesis. | |
| Tutor: | Giuseppina Gini (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 2-5 | |
| CFU: | 5-20 |
| Title: | Robotic prosthesis | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | The proposed projects in the development of an active hand prosthesis, novel in architecture since it considers anso the wrist. THe user interface is based on EMG signals.
All the projects can be turned into a thesis. | |
| Tutor: | Giuseppina Gini (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 2-3 | |
| CFU: | 5-20 |