Difference between revisions of "Master Level Theses"
DavidLaniado (Talk | contribs) m |
DavidLaniado (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 248: | Line 248: | ||
==== Ontologies and Semantic Web ==== | ==== Ontologies and Semantic Web ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Wiki Analysis ===== | ||
{{#ask: [[Category:ProjectProposal]] | {{#ask: [[Category:ProjectProposal]] | ||
| Line 264: | Line 266: | ||
format = template | | format = template | | ||
template = Template:ProjectProposalViz | template = Template:ProjectProposalViz | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 01:06, 30 May 2009
Here you can find proposals for master thesis (20 CFU for each student). See Project Proposals for other kinds of projects and theses.
Contents
Evolutionary Optimization and Stochastic Optimization
| Title: | Combinatorial optimization based on stochastic relaxation | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | The project will focus on the study, implementation, comparison and analysis of different algorithms for the optimization of pseudo-Boolean functions, i.e., functions defined over binary variables with values in R. These functions have been studied a lot in the mathematical programming literature, and different algorithms have been proposed [1]. More recently, the same problems have been faced in evolutionary computations, with the use of genetic algorithms, and in particular estimation of distribution algorithms [2,3]. Estimation of distribution algorithms are a recent meta-heuristic, where classical crossover and mutation operators used in genetic algorithms are replaced with operators that comes from statistics, such as sampling and estimation.
The focus will be on the implementation of a new algorithm able to combine different approaches (estimation and sampling, from one side, and exploitation of prior knowledge about the structure of problem, on the other), together with the comparison of the results with existing techniques that historically appear in different (and often separated) communities. Good coding (C/C++) abilities are required. Since the approach will be based on statistical models, the student is supposed to be comfortable with notions that come from probability and statistics courses. The project could require some extra effort in order to build and consolidate some background in math, especially in Bayesian statistics and MCMC techniques, such as Gibbs and Metropolis samplers [4]. The project can be extended to master thesis, according to interesting and novel directions of research that will emerge in the first part of the work. Possible ideas may concern the proposal of new algorithms able to learn existing dependencies among the variables in the function to be optimized, and exploit them in order to increase the probability to converge to the global optimum. Picture taken from http://www.ra.cs.uni-tuebingen.de/
| |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci ([1]), Luigi Malagò (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1-2 | |
| CFU: | 20-40 |
BioSignal Analysis
Analysis of the Olfactory Signal
| Title: | Computational Intelligence techniques to analyse the olfactory signal acquired by an electronic nose for cancer diagnosis | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | The electronic nose is an instrument able to detect and recognize odors, that is the volatile substances in the atmosphere or emitted by the analyzed substance. This device can react to a gas substance by providing signals that can be analyzed to classify the input. It is composed of a sensor array (MOS sensors, in our case) and a pattern classification system based on machine learning techniques. Each sensor reacts in a different way to the analyzed substance, providing multidimensional data that can be considered as a unique olfactory blueprint of the analyzed substance. We have already tested the use of the electronic nose as diagnostic tool for lung cancer; boosted from the very satisfactory results that we have achieved by these analysis, we want to investigate the possibility of diagnosing other types of cancer and to improve the current computation intelligence techniques.
The project is done in collaboration with the Istituto dei Tumori, Milano.
| |
| Tutor: | Andrea Bonarini (email), Matteo Matteucci (email), Rossella Blatt (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime (a new acquisition phase will start in March) | |
| Number of students: | 1-2 | |
| CFU: | 20 |
Sleep Staging
| Title: | Development of a computer-assisted CAP (Sleep cyclic alternating pattern) scoring method | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | In 1985, Terzano describes for the first time the Cyclic Alternating Pattern [2] during sleep and, nowadays, CAP is widely accepted by the medical community as basic analysis of sleep. The CAP evaluation is of fundamental importance since it represents the mechanism developed by the brain evolution to monitor the inner and outer world and to assure the survival during sleep. However, visual detection of CAP in polisomnography (i.e., the standard procedure) is a slow and time-consuming process. This limiting factor generates the necessity of new computer-assisted scoring methods for fast CAP evaluation. This thesis deals with the development of a Decision Support System for CAP scoring based on features extraction at multi-system level (by statistical and signal analysis) and Pattern Recognition or Machine Learning approaches. This may allow the automatic detection of CAP sleep and could be integrated, through reinforcement learning techniques, with the corrections given by physicians.
| |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Martin Mendez (email), Anna Maria Bianchi (email), Mario Terzano (Ospedale di Parma) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1-2 | |
| CFU: | 20 |
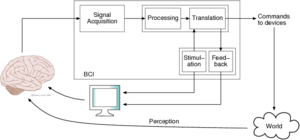
Brain-Computer Interface
| Title: | Recognition of the user's focusing on the stimulation matrix | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | A P300-based BCI stimulates the user continuously, and the detection of a P300 designates the choice of the user. When the user is not paying attention to the interface, false positives are likely. The objective of this work is to avoid this problem; the analysis of the electroencephalogram (EEG) over the visual cortex (and possibly an analysis of P300s or of other biosignals) should tell when the user is looking at the interface.
| |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Bernardo Dal Seno (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1-2 | |
| CFU: | 20 |
| Title: | Creation of new EEG training by introduction of noise | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | A BCI must be trained on the individual user in order to be effective. This training phase require recording data in long sessions, which is time consuming and boring for the user. The aim of this project is to develop algorithm to create new training EEG (electroencephalography) data from existing ones, so as to speed up the training phase.
| |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Bernardo Dal Seno (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1 | |
| CFU: | 20 |
| Title: | Real-time removal of ocular artifact from EEG | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | In a BCI based on electroencephalogram (EEG), one of the most important sources of noise is related to ocular movements. Algorithms have been devised to cancel the effect of such artifacts. The project consists in the in the implementation in real time of an existing algorithm (or one newly developed) in order to improve the performance of a BCI.
| |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Bernardo Dal Seno (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1 | |
| CFU: | 10-20 |
| Title: | Aperiodic visual stimulation in a VEP-based BCI | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | Visual-evoked potentials (VEPs) are a possible way to drive the a BCI. This projects aims at maximizing the discrimination between different stimuli.
| |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Bernardo Dal Seno (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1 | |
| CFU: | 20 |
| Title: | Driving an autonomous wheelchair with a P300-based BCI | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | This project pulls together different Airlab projects with the aim to drive an autonomous wheelchair (LURCH) with a BCI, through the development of key software modules. The work will be validated with live experiments.
| |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Bernardo Dal Seno (email) | |
| Start: | November 2008 | |
| Number of students: | 1 | |
| CFU: | 5-20 |
| Title: | Online automatic tuning of the number of repetitions in a P300-based BCI | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | In a P300-based BCI, (visual) stimuli are presented to the user, and the intention of the user is recognized when a P300 potential is recognized in response of the desired stimulus. In order to improve accuracy, many stimulation rounds are usually performed before making a decision. The exact number of repetitions depends on the user and the goodness of the classifier, but it is usually fixed a-priori. The aim of this project is to adapt the number of repetitions to changing conditions, so as to achieve the maximum accuracy with the minimum time.
The work will be validated with live experiments.
| |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Bernardo Dal Seno (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1 | |
| CFU: | 5-20 |
Machine Learning
| Title: | Statistical inference for phylogenetic trees | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | The project will focus on the study, implementation, comparison and analysis of different statistical inference techniques for phylogenetic trees. Phylogenetic trees [1, 2] are evolutionary trees used to represent the relationships between different species with a common ancestor. Typical inference task concern the construction of a tree starting from DNA sequences, involving both the choice of the topology of the tree (i.e., model selection) and the values of the parameters (i.e., model fitting). The focus will be a probabilistic description of the tree, given by the introduction of stochastic variables associated to both internal nodes and leaves of the tree.
The project will focus on the understanding of the problem and on the implementation of different algorithms, so (C/C++ or Matlab or R) coding will be required. Since the approach will be based on statistical models, the student is supposed to be comfortable with notions that come from probability and statistics courses. The project is thought to be extended to master thesis, according to interesting and novel directions of research that will emerge in the first part of the work. Possible ideas may concern the proposal and implementation of new algorithms, based on recent approaches to phylogenetic inference available in the literature, as in [3] and [4]. In this case the thesis requires some extra effort in order to build and consolidate some background in math in oder to understand some recent literature, especially in (mathematical) statistics and, for example, in the emerging field of algebraic statistics [5]. Picture taken from http://www.tolweb.org/tree/
| |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci ([11]), Luigi Malagò (email) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1-2 | |
| CFU: | 20-40 |
| Title: | Reinforcement Learning in Poker | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | In this years, Artificial Intelligence research has shifted its attention from fully observable environments such as Chess to more challenging partially observable ones such as Poker.
Up to this moment research in this kind of environments, which can be formalized as Partially Observable Stochastic Games, has been more from a game theoretic point of view, thus focusing on the pursue of optimality and equilibrium, with no attention to payoff maximization, which may be more interesting in many real-world contexts. On the other hand Reinforcement Learning techniques demonstrated to be successful in solving both fully observable problems, single and multi-agent, and single-agent partially observable ones, while lacking application to the partially observable multi-agent framework. This research aims at studying the solution of Partially Observable Stochastic Games, analyzing the possibility to combine the Opponent Modeling concept with the well proven Reinforcement Learning solution techniques to solve problems in this framework, adopting Poker as testbed. | |
| Tutor: | Marcello Restelli (restelli-AT-elet-DOT-polimi-DOT-it) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1-2 | |
| CFU: | 20-40 |
| Title: | EyeBot | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | TORCS is a state-of-the-art open source racing simulator that represents an ideal bechmark for machine learning techniques. We already organized two successfull competitions based on TORCS where competitors have been asked to develop a controller using their preferred machine learning techniques. So far, the controller developed for TORCS used as input only information extracted directly from the state of the game. The goal of this project is to extend the existing controller API (see here) to use the visual information (e.g. the screenshots of the game) as input to the controllers. A successfull project will include both the development of the API and some basic imaga preprocessing to extract information from the images. | |
| Tutor: | Daniele Loiacono (loiacono-AT-elet-DOT-polimi-DOT-it), Alessandro Giusti (giusti-AT-elet-DOT-polimi-DOT-it), and Pierluigi Taddei (taddei-AT-elet-DOT-polimi-DOT-it) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1 to 2 | |
| CFU: | 20 |
| Title: | SmarTrack | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | The generation of customized game content for each player is an attractive direction to improve the game experience in the next-generation computer games. In this scenario, Machine Learning could play an important role to provide automatically such customized game content.
The goal of this project is to apply machine learning techniques for the generation of customized tracks in TORCS, a state-of-the-art open source racing simulator. The project include different activities: the automatic generation of tracks, the section of relevant features to characterize a track and the analysis of an interest measure. | |
| Tutor: | Daniele Loiacono (loiacono-AT-elet-DOT-polimi-DOT-it) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1 to 2 | |
| CFU: | 20 |
| Title: | Automatic generation of domain ontologies | [[Image:|center|300px]] |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | This thesis to be developed together with Noustat S.r.l., who are developing research activities directed toward the optimization of knowledge management services, in collaboration with another company operating in this field. This project is aimed at removing the ontology building bottleneck, long and expensive activity that usually requires the direct collaboration of a domain expert. The possibility of automatic building the ontology, starting from a set of textual documents related to a specific domain, is expected to improve the ability to provide the knowledge management service, both by reducing the time-to-application, and by increasing the number of domains that can be covered. For this project, unsupervised learning methods will be applied in sequence, exploiting the topological properties of the ultra-metric spaces that emerge from the taxonomic structure of the concepts present in the texts, and associative methods will extend the concept network to lateral, non-hierarchical relationships. | |
| Tutor: | Matteo Matteucci (email), Andrea Bonarini (email) | |
| Start: | before November 30th | |
| Number of students: | 1-2 | |
| CFU: | 20 |
Ontologies and Semantic Web
Wiki Analysis
| Wiki Page: | 3D Scene Understanding | |
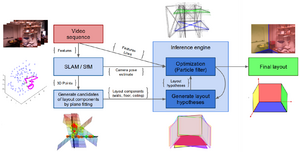
| Title: | 3D Indoor scene understanding and layout reconstruction for a mobile robot in collaboration with UnimiB | |
| Description: | The proposed project aims to reconstruct the 3D structural layout of an indoor environment perceived by a mobile robot. From the sensorial data, the robot should be able to reconstruct a geometrical structure of an indoor environment (e.g., an office).
Methods for indoor layout reconstruction must be significantly more tolerant to missing data than their outdoor counterparts, since environments such as offices and apartments exhibit extremely high levels of clutter, which typically results in heavy occlusions of walls and other structures of interest, large-scale artifacts, noise and missing data. The proposed work will be developed in collaboration with IRALAB, the Robotics Lab of University of Milano Bicocca. The work will be based on an existing project, Free Your Camera (http://www.ira.disco.unimib.it/research/robotic-perception-research/free-your-camera-3d-indoor-scene-understanding-from-arbitrary-camera-motion/) and will be part of a robotic framework based on with ROS and in development at IRALAB. | |
| Tutor: | [[FrancescoAmigoni | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 February 2015 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 10 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | Robotics |
| Wiki Page: | A firefox extension for semantic annotations | |
| Title: | A Firefox extension for semantic annotations | |
| Description: | Aim of this project is to develop a Firefox extension, to allow a community of users to annotate resources on the Web using a shared RDF vocabulary.
While browsing the Web, a user should be able to visualize the annotations relative to the page they are visiting, and to add new annotations as well. | |
| Tutor: | [[DavidLaniado | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | ||
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Social Software and Semantic Web | |
| Research Topic: | Semantic Annotations |
| Wiki Page: | AI in Racing Games | |
| Title: | AI in Racing Games | |
| Description: | This project is focused on TORCS, a state-of-the-art open source racing simulator. From one hand, TORCS represents an ideal bechmark to study Computational Intelligence techniques. On the other hand, Computational Intelligence techniques could be used to improve the game experience in this kind of games. Several projects and theses are available on this topic, please contact us for additional information.
References:
| |
| Tutor: | [[DanieleLoiacono | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Computational Intelligence and Games | |
| Research Topic: | Computational Intelligence and Games |
| Wiki Page: | Accurate AR Marker Location | |
| Title: | C++ Library for accurate marker location based on subsequent pnp refinements | |
| Description: | ARTags, QR codes, Data Matrix, are visual landmark used for augmented reality, but they could be used for robotics as well. A thesis has already been done on using data matrix for robot localization and mapping, but improvements are required in terms generality, accuracy and robustness of the solution. The goal is thuss to:
Material:
Expected outcome:
Required skills or skills to be acquired:
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 January 2015 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 10 | |
| Research Area: | Computer Vision and Image Analysis | |
| Research Topic: | None |
| Wiki Page: | Annotation aggregators from social applications | |
| Title: | Annotation aggregators from social applications | |
| Description: | Annotations are metadata published about a resource, such as tags in del.icio.us, comments on stumbleupon.com, or twines on Twine.com. One of the main problems of these annotations is that they are not expressed in a standard format: thus, any tool trying to aggregate information from these sources should be able to access each one of them in a different way.
The purpose of this project is to develop translation tools for different social annotation systems, collect their data in a common format (expressed using an ontology), and show them through a unique user interface, able to display different annotations (i.e. geo coordinates, dates, tags, etc.) in different ways. Moreover, tests and evaluations should be performed on this aggregator to show how efficient the queries are when performed on-the-fly or from an intermediate knowledge base. | |
| Tutor: | [[DavideEynard | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | ||
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Social Software and Semantic Web | |
| Research Topic: | Semantic Annotations |
| Wiki Page: | Aperiodic visual stimulation in a VEP-based BCI | |
| Title: | Aperiodic visual stimulation in a VEP-based BCI | |
| Description: | Visual-evoked potentials (VEPs) are a possible way to drive the a Brain-Computer Interface (BCI). This projects aims at maximizing the discrimination between different stimuli by using numerical codes derived from techniques of digital telecommunications.
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 | |
| CFU: | 5 | |
| Research Area: | BioSignal Analysis | |
| Research Topic: | Brain-Computer Interface |
| Wiki Page: | Autistic Children Play Robot | |
| Title: | Autistic Children Play Robot | |
| Description: | Within a Polisocial project we will have to implement a robot suitable to play autonomously with autistic children that will interact with it and a game system by gestures.
The thesis will explore some of the aspects of the problem, eventually participating to the production of prototypes to be tested with real users. The thesis gives the possibility to develop a robot with special requirements, and to work with gesture interpretation by using devices such as Kinect or the WII Mote. The work is done in an interdisciplinary group including care givers and designers. | |
| Tutor: | [[AndreaBonarini | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 20 January 2015 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 20 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | Robogames |
| Wiki Page: | Automatic Content Generation in Computer Games | |
| Title: | Automatic Content Generation in Computer Games | |
| Description: | The generation of customized game content for each player is an attractive direction to improve the game experience in the next-generation computer games. In this scenario, Machine Learning could play an important role to provide automatically such customized game content. Several projects and theses are available on this topic, please contact us for additional information.
Picture taken from http://gar.eecs.ucf.edu/
| |
| Tutor: | [[DanieleLoiacono | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Computational Intelligence and Games | |
| Research Topic: | Computational Intelligence and Games |
| Wiki Page: | Automatic Differentiation Techniques for Real Time Kalman Filtering | |
| Title: | Evaluation of Automatic Differentiation Techniques for Gauss-Newton based Simultaneous Localization and Mapping | |
| Description: | In Gauss-Newton non linear optimization one of the most tedious part is computing Jacobians. At the AIRLab we have developed a framework for non linear Simultaneous Localization and Mapping suitable for different motion models and measurement equations, but any time you need to change something you need to recompute the required Jacobian. Automatic differentiation is a tool for the automatic differentiation of source code either at compiling time or at runtime; we are interested in testing these techniques in the software we have developed and compare their performance with respect to (cumbersome) optimized computation.
Material
Expected outcome: New modules implementations based on automatic differentiation A comparison between the old stuff and new approach Required skills or skills to be acquired:
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 January 2015 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 10 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | None |
| Wiki Page: | Automatic generation of domain ontologies | |
| Title: | Automatic generation of domain ontologies | |
| Description: | This thesis to be developed together with Noustat S.r.l. (see http://www.noustat.it), who are developing research activities directed toward the optimization of knowledge management services, in collaboration with another company operating in this field. This project is aimed at removing the ontology building bottleneck, long and expensive activity that usually requires the direct collaboration of a domain expert. The possibility of automatic building the ontology, starting from a set of textual documents related to a specific domain, is expected to improve the ability to provide the knowledge management service, both by reducing the time-to-application, and by increasing the number of domains that can be covered. For this project, unsupervised learning methods will be applied in sequence, exploiting the topological properties of the ultra-metric spaces that emerge from the taxonomic structure of the concepts present in the texts, and associative methods will extend the concept network to lateral, non-hierarchical relationships. | |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | ||
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 20 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Machine Learning |
| Wiki Page: | Barking Robots | |
| Title: | Barking Robots | |
| Description: | Aim of this project is the development of a robot that can operate autonomously at exhibitions and malls to attract people to a given location, by showing interesting behaviors and interacting with people.
The robot first exhibition has been at Robotica 2009, within HI-Tech Expo at Fiera di Milano, on November 23-25, 2009. Here, the robot had to go around in an area delimited by a white stripe and contact verbally and with gestures people entering the area, in order to attract them to the booth. Behaviors and gestures have still to be developed to come to an interesting and robust demo at next Robotica, or at other ehibits (e.g. at the Museo della Scienza of Milan). | |
| Tutor: | [[AndreaBonarini | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 25 February 2012 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | Robot development |
| Wiki Page: | Behavior recognition from visual data | |
| Title: | Behavior recognition from visual data | |
| Description: | In the literature several approaches have been used to model observed behaviors and these date back to early approaches in animal behavior analysis (Baum and Eagon, 1967)(Colgan, 1978). Nowadays several techniques are used and they can be roughly classified as: State space models, Automata (e.g., Finite State Machines, Agents, etc.), Grammars (e.g., strings, T-Patterns, etc.), Bayeasian models (e.g., Hidden Markov Models), and Dynamic State Variables. The work will leverage on a huge corpus of techniques to devise the most suitable for behavior recognition from visual data. We exclude from the very beginning any deterministic approach being the phenomenon under observation complex and affected by noisy observations. The focus will be mainly of the use of dynamic graphical models (Ghahramani, 1998) and the application of bottom up learning techniques (Stolcke and Omohundro, 1993)(Stolcke and Omohundro, 1994) for model induction.
Material:
Expected outcome:
Required skills or skills to be acquired:
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 April 2012 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 20 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Machine Learning | |
| Research Topic: | None |
| Wiki Page: | BringMeHome | |
| Title: | BringMeHome | |
| Description: | ||
| Tutor: | [[AndreaBonarini | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 30 March 2013 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 2 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | E-2? - A robot for exhibitions |
| Wiki Page: | CAN Bus bootloader for STM32 microcontrollers | |
| Title: | CAN Bus bootloader for STM32 microcontrollers | |
| Description: | JOINT PROJECT with the Embedded Systems group (contact: Patrick Bellasi http://home.dei.polimi.it/bellasi/)
In order to speed up the development and the maintenance of embedded applications, a way to update the firmware on a microcontroller without the need of connecting cables or programmers can be very handy. We are developing a framework for rapid prototyping of low-cost robots, with smart devices that exchange data on a CAN bus network. The CAN bus bootloader is one of the components we need for this project, enabling remote firmware upgrades of all the devices connected to the CAN network. This project aims to develop a CAN bus bootloader for STM32 ARM Cortex-M3 microcontrollers, and eventually for other architectures. | |
| Tutor: | [[AndreaBonarini | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 March 2012 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 2 - 5 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | Robot development |
| Wiki Page: | Cognitive SLAM | |
| Title: | Cognitive SLAM | |
| Description: | We have developed a system that is able to detect, recognize and track objects in an image taken from a low cost robot equipped with a IMU and a low cost camera. The system is capable to detect and recognize objects using a user defined fuzzy tree classifier. However the system performance is heavily dependent on high level feature extraction, such as geometric features. The problem is non trivial due to noisy low cost camera and changes in the light conditions. The aim of this project is to improve the feature extraction and description process, both in performance and quality, possible adding a more complete description or others type of features. The long term aim of the research is to have an autonomuos robot capable to create a semantic map of the envirorment, localize himself , make inference on the map, navigate into the envirorment using the objects as landmarks.
No special skills are required, except basic c and object oriented programming. | |
| Tutor: | [[AndreaBonarini | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 January 2015 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Robotics | |
| Research Topic: | SLAM, Feature Extraction |
| Wiki Page: | Combinatorial optimization based on stochastic relaxation | |
| Title: | Combinatorial optimization based on stochastic relaxation | |
| Description: | The project will focus on the study, implementation, comparison and
analysis of different algorithms for the optimization of pseudo-Boolean functions, i.e., functions defined over binary variables with values in R. These functions have been studied a lot in the mathematical programming literature, and different algorithms have been proposed (1). More recently, the same problems have been faced in evolutionary computations, with the use of genetic algorithms, and in particular estimation of distribution algorithms (2,3). Estimation of distribution algorithms are a recent meta-heuristic, where classical crossover and mutation operators used in genetic algorithms are replaced with operators that come from statistics, such as sampling and estimation. The focus will be on the implementation of a new algorithm able to combine different approaches (estimation and sampling, from one side, and exploitation of prior knowledge about the structure of problem, on the other), together with the comparison of the results with existing techniques that historically appear in different (and often separated) communities. Good coding (C/C++) abilities are required. Since the approach will be based on statistical models, the student is supposed to be comfortable with notions that come from probability and statistics courses. The project could require some extra effort in order to build and consolidate some background in math, especially in Bayesian statistics and MCMC techniques, such as Gibbs and Metropolis samplers (4). The project can be extended to master thesis, according to interesting and novel directions of research that will emerge in the first part of the work. Possible ideas may concern the proposal of new algorithms able to learn existing dependencies among the variables in the function to be optimized, and exploit them in order to increase the probability to converge to the global optimum. Picture taken from http://www.ra.cs.uni-tuebingen.de/ Bibliography
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Machine Learning | |
| Research Topic: | Information Geometry, Stochastic Optimization |
| Wiki Page: | Combining Estimation of Distribution Algorithms and other Evolutionary techniques for combinatorial optimization | |
| Title: | Combining Estimation of Distribution Algorithms and other Evolutionary techniques for combinatorial optimization | |
| Description: | The project will focus on the study, implementation, comparison and analysis of different algorithms for combinatorial optimization using techniques and algorithms proposed in Evolutionary Computation. In particular we are interested in the study of Estimation of Distribution Algorithms (1,2,3,4), a recent meta-heuristic, often presented as an evolution of Genetic Algorithms, where classical crossover and mutation operators, used in genetic algorithms, are replaced with operators that come from statistics, such as sampling and
estimation. The focus will be on the implementation of new hybrid algorithms able to combine estimation of distribution algorithms with different approaches available in the evolutionary computation literature, such as genetic algorithms and evolutionary strategies, together with other local search techniques. Good coding (C/C++) abilities are required. Some background in combinatorial optimization form the "Fondamenti di Ricerca Operativa" is desirable. The project could require some effort in order to build and consolidate some background in MCMC techniques, such as Gibbs and Metropolis samplers (4). The project could be extended to master thesis, according to interesting and novel directions of research that will emerge in the first part of the work. Computer vision provides a large number of optimization problems, such as new-view synthesis, image segmentation, panorama stitching and texture restoration, among the others, (6). One common approach in this context is based on the use of binary Markov Random Fields and on the formalization of the optimization problem as the minimum of an energy function expressed as a square-free polynomial, (5). We are interested in the proposal, comparison and evaluation of different Estimation of Distribution Algorithms for solving real world problems that appear in computer vision. Pictures taken from http://www.genetic-programming.org and (6) Bibliography
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 10 | |
| Research Area: | Machine Learning | |
| Research Topic: | Evolutionary Computation, Stochastic Optimization |
| Wiki Page: | Comparison of State of the Art Visual Odometry Systems | |
| Title: | A Comparison of State of the Art Visual Odometry Systems (Monocular and Stereo) | |
| Description: | Visual odometry is the estimation of camera(s) movement from a sequence of images. In case we deal with a single camera system we have Monocular Visual Odometry; in case we have more cameras we have a Stero Visual Odometry. The goal of the thesis is to review the state of the art on in visual odometry, classify existing approaches and compare their implementations (many of the algorithms have online source code available).
Material
Expected outcome:
Required skills or skills to be acquired:
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 January 2015 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 10 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Computer Vision and Image Analysis | |
| Research Topic: | None |
| Wiki Page: | Creation of new EEG training by introduction of noise | |
| Title: | Creation of new EEG training by introduction of noise | |
| Description: | A Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) must be trained on the individual user in order to be effective. This training phase require recording data in long sessions, which is time consuming and boring for the user. The aim of this project is to develop algorithm to create new training EEG (electroencephalography) data from existing ones, so as to speed up the training phase.
| |
| Tutor: | [[MatteoMatteucci | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | BioSignal Analysis | |
| Research Topic: | Brain-Computer Interface |
| Wiki Page: | Data Mining in Computer Games | |
| Title: | Data Mining in Computer Games | |
| Description: | Today a lot of data can be extracted from popular games. The analysis of such data allow to discover a lot of interesting information about players, the game and the interaction between the game and different type of players.
Several theses and projects are available on this topic and involve different games: TORCS, Unreal Tournament and Quake Live. Please contact us for additional information.
| |
| Tutor: | [[DanieleLoiacono | ]] (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , … further resultswarning.png
| |
| Start: | 1 October 2009 | |
| Students: | 1 - 2 | |
| CFU: | 5 - 20 | |
| Research Area: | Computational Intelligence and Games | |
| Research Topic: | Computational Intelligence and Games |
… further resultswarning.png"Ontologies and Semantic Web" is not in the list of possible values (Affective Computing, Agents - Multiagent Systems - Agencies, BioSignal Analysis, Computational Intelligence and Games, Computer Vision and Image Analysis, E-Science, Machine Learning, Philosophy of Artificial Intelligence, Robotics, Social Software and Semantic Web) for this property.
Robotics
| Title: | Robot games | |
|---|---|---|
| Description: | The goal of this activity is to develop an interactive game with robots using commercial devices such as the WII Mote (see the Robogames page)
Projects are available in different areas:
These projects allow to experiment with real mobile robots and real interaction devices. Parts of these projects can be considered as course projects. These projects can also be extended to cover course projects. | |
| Tutor: | Andrea Bonarini (bonarini-AT-elet-DOT-polimi-DOT-it) | |
| Start: | Anytime | |
| Number of students: | 1-2 | |
| CFU: | 7.5-20 |